
The plastic prototyping, modeling and “bridge-to-production” tooling technology is rapidly changing. Texas Injection Molding maintains in-house and an outside network of industry leading providers to deliver our customers a broad range of material, size and processes to model and replicate performance as close as possible to production units. We offer concept review, design consultancy, material selection, prototype and low volume production for projects that are planned to increase to volume production.
We understand the requirements of high-volume manufacturing and offer design for manufacturing experience to ensure cost effective manufacturable products as products are delivered from prototype to high volume production.
Rapid Prototyping & 3D Printing
Texas Injection Molding can save you money and time with our 3D printing capabilities.
Our plastic prototypes are high quality and are made with accuracy and consistency. Our network of providers has the expertise to consult on your design and make the appropriate changes easily and at a low cost.
Rapid Prototyping is an additive manufacturing technology and comprises of techniques that can speed up the time it takes to fabricate a prototype with flexibility. It all starts with a design from modeling or CAD software. And then with 3D printing we can interpret the CAD data and create the 3D model.
Texas Injection Molding works with you take your design to realization.
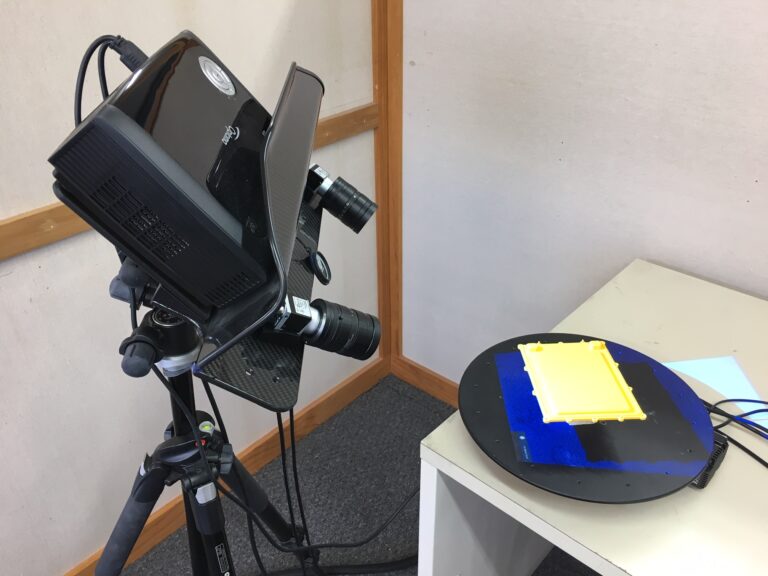

3D Scanning
Overview: 3D Scanning or 3D Imaging is a process where the digital shape an object can be measured with non-contact imaging systems. 3D laser scanners collect millions of data points in three dimensional space called a point cloud. This method provides extremely accurate measurements of these points in X, Y, Z positions. The resulting digital image can be drafted or modeled in CAD systems to create a model that can be reproduced or edited to the desired geometry. 3D scanning is very useful in reverse engineering where legacy parts produced prior to digital technology or parts with no CAD model can be created and used for documentation, modeling, 3D printing, production tooling, or quality inspection.
Send us parts and we can scan them and return the parts with digital files in many native formats:
• AutoCad
• Autodesk Inventor
• CATIA
• ProE
• SolidWorks
• UG
• And others
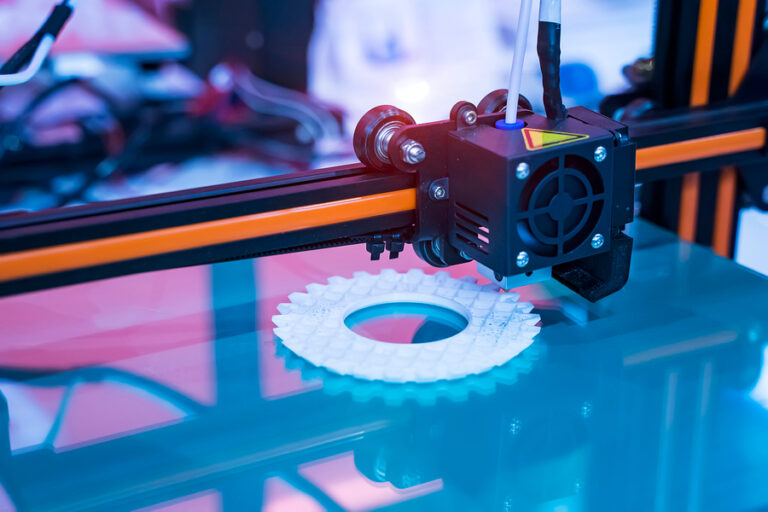

Fuse Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Overview: Fused Deposition Modeling is a low-cost prototyping process that allows for mechanically strong parts to be created.
Materials Used & Part Characteristics: FDM is noted for it wide range of material options.
Some of the major materials include ABS, PLA, Nylon (PA6 / PA 66), PETG and TPU materials are melted and extruded in round layers to build up parts. Because the extrusion is round, sharp corners and other fine features are limited.
Where used: Often used in creating fixtures due to low cost and strong mechanical strength. Also used in early stage prototypes or concept models.
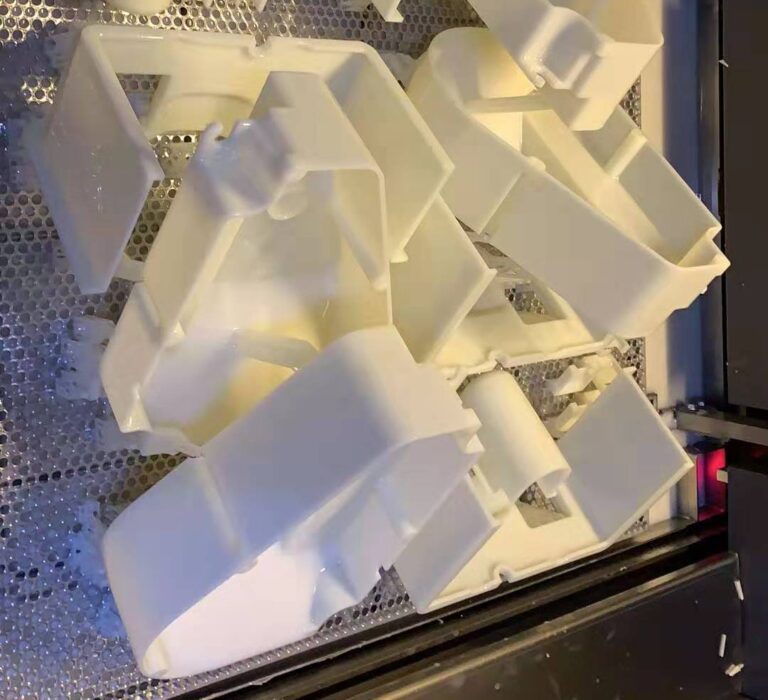

Stereolithography (SL)
Overview: SLA provides the ability to print very tight tolerances, smooth surface finishes and high resolution of small features. The main downside is the lower mechanical strength and not suitable for exposure to UV or sunlight.
Materials Used & Part Characteristics: Photopolymer (UV
curable) epoxy or acrylic-base materials are used to manufacture fine resolution cosmetic parts.
Where used: Cosmetic prototypes that require high resolution details and smooth surface finishes. Also used in molds for casting other materials:
• Casting and Modeling
• 3D Printing

Selective Laser Sintering (LS)
Overview: SLS provides the ability to generated complex geometry, highly accurate and durable parts that are suitable for use as functional parts.
Materials Used & Part Characteristics: PA12 is the most common, but PA6 and PA11 are also common. ABS, PC PMMA, POM and some TPU’s and compounds with additives are also available. Nylons offer strong, heat resistant and durable parts.
Where used: SLS parts are routinely used to test form and function in prototypes or in low volume production.

Polyjet
Overview: Polyjet provides the ability to print multi-material, highly accurate and tight tolerance parts. Parts can be black, white, transparent and have a range of softness from rubberlike to rigid in the same part.
Materials Used & Part Characteristics: A variety of UV curable polymers allow for simulation for a range of material substitutes. Polyjet has soft materials in Shore A hardness from 25 – 95, stiff but flexible materials similar in feel too polypropylene, and rigid materials with characteristics similar to ABS. Corners designed to be sharp may have a slight radius.
Where used: Polyjet is often used for manufacturing parts with gaskets, seals or need for soft grips combined with hard plastics. Combining colored and transparent resins also allow for illustration and creative design. Polyjet is also used for creating wax molds for investment castings
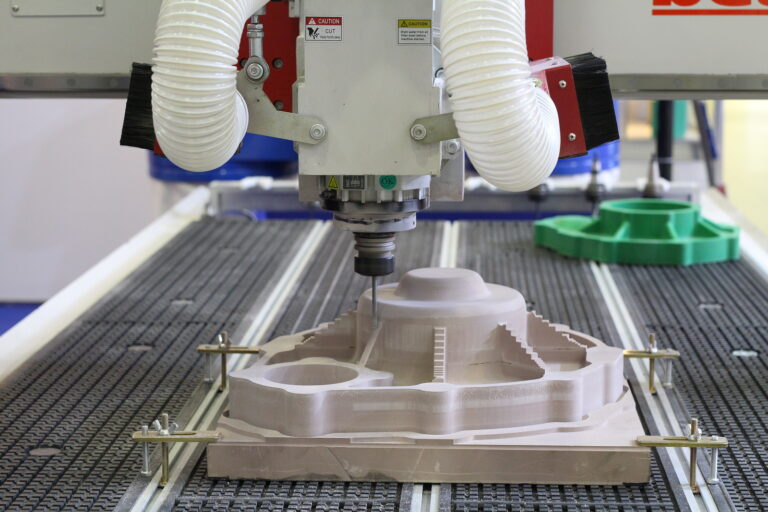
Machining & Post process finishing
Overview: Machining is a subtractive process where we start with a solid block of material and remove material to leave a finished part. Machining allows for use of specific grades of plastics or metals that are not available for printing.
Materials Used & Part Characteristics: A wide range of polymers, metals and alloys.
Where used: Machining especially useful in evaluating mechanical performance in specific materials prior to finalizing part geometry and material specifications. Machining is suitable for prototyping and low volume production.
Looking to get started? Check out our Project Information guide.
For more information and ordering prototyping please visit our prototype website: Texas Prototype
